![]() Kila mtu ana uwezekano wa kujua mfano wa kawaida wa nondo au kipepeo – proboscis kama majani kufikia nekta iliyofichwa ndani ya maua. Idadi kubwa ya Lepidoptera wametofautiana pamoja na mionzi ya mimea ya angiosperm, kuwa moja ya utaratibu tofauti na tele wa maisha duniani. This paradigm however does not apply to the Micropterigidae, which represent not only the most basal lineage of the Lepidoptera, but are one of three families that have retained mandibles for grinding pollen or spores and rely on bryophytes, decaying organic matter or fungi as a larval host. Prior assumptions as to the diversity of this group were based on the vast age of the lineage (110 million years) and a buildup of ancient genera. A recent paper on the Japanese species of Micropterigidae by Yume Imada and her colleagues at Kyoto University provides evidence to the contrary and applies molecular techniques to test the hypothesis of allopatric speciation without niche shift.
Kila mtu ana uwezekano wa kujua mfano wa kawaida wa nondo au kipepeo – proboscis kama majani kufikia nekta iliyofichwa ndani ya maua. Idadi kubwa ya Lepidoptera wametofautiana pamoja na mionzi ya mimea ya angiosperm, kuwa moja ya utaratibu tofauti na tele wa maisha duniani. This paradigm however does not apply to the Micropterigidae, which represent not only the most basal lineage of the Lepidoptera, but are one of three families that have retained mandibles for grinding pollen or spores and rely on bryophytes, decaying organic matter or fungi as a larval host. Prior assumptions as to the diversity of this group were based on the vast age of the lineage (110 million years) and a buildup of ancient genera. A recent paper on the Japanese species of Micropterigidae by Yume Imada and her colleagues at Kyoto University provides evidence to the contrary and applies molecular techniques to test the hypothesis of allopatric speciation without niche shift.
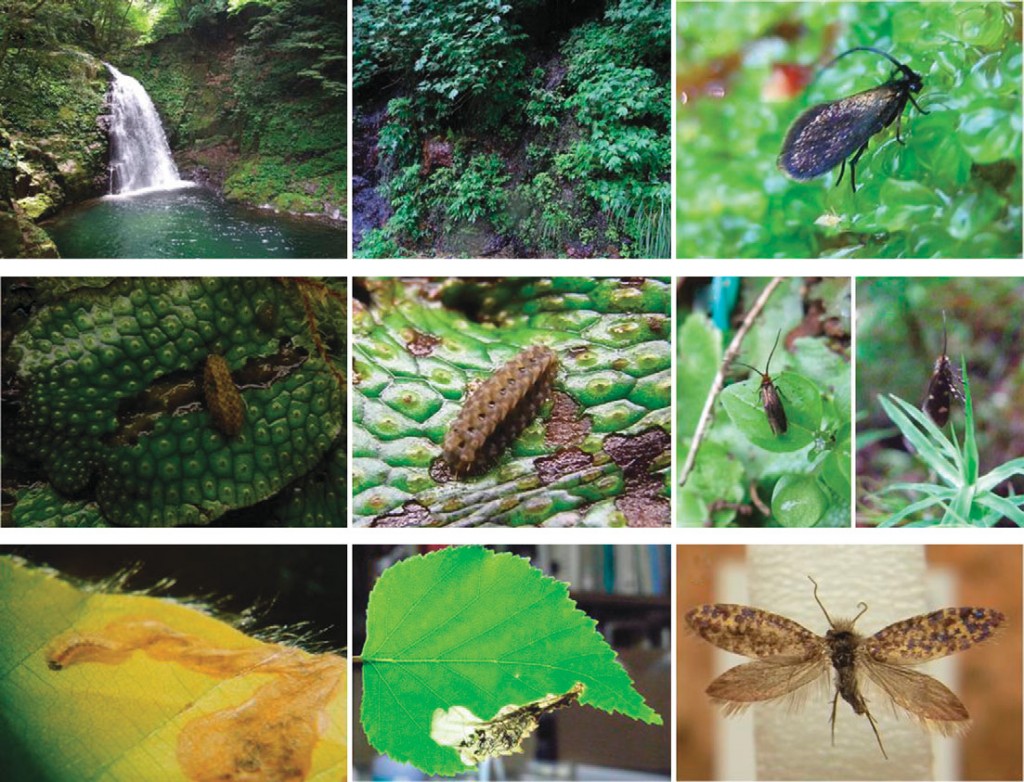
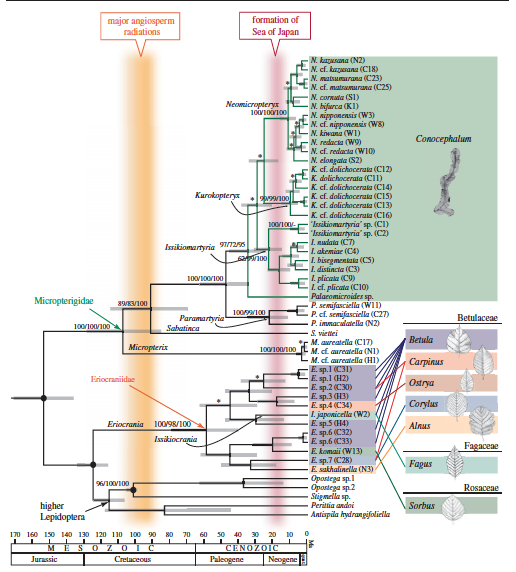
The authors traveled to 46 localities across the Japanese archipelago and collected all 16 known endemic species, a few new species, and quite possibly a new genus. Finding these moths in the wild is not all that difficult if you know how to find the habitat and how not to fall off slippery rocks; but once you do find the spot the moths can be abundant. Micropterigidae are unsurprisingly associated with their bryophytes, which occur in moist habitats along streams and rivers. The very nature of a minute and slow moving animal in isolated pockets lends itself to allopatric speciation. Many microlepidoptera barely fly off of their host plant and even when they do they are not known for long distance dispersal. While the majority of genera and species are completely isolated across Japan there are a few instances where the genus Paramartyria occurs within populations of Issikiomartyria. While it is unknown precisely how these species might partition their host resources it is very likely to be a temporal difference in life-cycles. Here in California there is a vastly confusing complex of Apodemia butterflies that comprise a handful of species and (bila shaka) subspecies that are partitioned on the same plant by spring and fall breeding seasons.
Impressively, every micropterigid collected as larvae were found only on the Conocephalum conicum species of liverwort, in spite of there being up to fourteen other bryophyte species available in the same habitat. It had been long understood that the Asian Micropterigidae fed on liverworts, but the extent of their host specificity had never been quantified. Feeding behavior appears to be the same across all of the surveyed species, with caterpillars grazing along the top of the bryophytes consuming the upper tissue layers.
Phylogenetic analysis of the COI, 18S and EF-1α genes generated highly congruent trees using multiple analytical methods. It appears that the endemic Japanese genera and the Conocephalum feeding strategy form a well supported monophyletic clade (in green). Kwa kifupi, the radiation of the host-specific Micropterigidae coincide with the separation, uplift, and isolation of the Japanese landmass roughly 20 miaka milioni iliyopita. It could not have been difficult to propose the hypothesis that the diversity of the Japanese Micropterigidae could only be as old as the island itself; and it’s also an accepted fact today that allopatric speciation happens more commonly than once thought. But quantifying these theories and explaining how and why this happens is exactly what science is about.
Literature Cited
Imada Y, Kawakita A, & Kato M (2011). Allopatric distribution and diversification without niche shift in a bryophyte-feeding basal moth lineage (Lepidoptera: Micropterigidae). Proceedings. Biological sciences / The Royal Society, 278 (1721), 3026-33 PMID: 21367790
Scoble, MJ. (1992). Lepidoptera: Fomu, function, and diversity. Oxford Univ. Press.


Inavutia. Note that the single species [to my knowledge] of Micropterygidae in the western US, Epimartynia pardella, also feeds on Conocephalum conicum. [unpublished obs.] Don’t know if it nests within the Japanese species, but I’d question that the japanese species had to differentiate within the confines of the present archipelago…